ODrive Motors
Below is general characteristics and performance numbers of the motors sold on the ODrive shop. Note that all performance figures are approximate, and real-world performance will depend on your particular application and cooling solution.
Motor Characteristics
M8325s 100KV
Specification |
Value |
Unit |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Speed Constant |
100 |
RPM/V [1] |
|
Torque Constant |
0.083 |
Nm/A [2] |
|
Speed / Torque Gradient |
43.53 |
RPM/Nm |
|
Pole Pairs |
20 |
||
Phase Resistance |
24 |
mΩ |
Phase-neutral |
Phase Inductance |
9.9 |
uH |
Phase-neutral |
Continuous Current |
40 60 |
A A |
Free Air Forced Air |
Peak Current |
80 |
A |
3-second |
Thermistor |
NTC 10k 3435 |
D6374 150KV
Specification |
Value |
Unit |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Speed Constant |
150 |
RPM/V [1] |
|
Torque Constant |
0.055 |
Nm/A [2] |
|
Speed / Torque Gradient |
159.54 |
RPM/Nm |
|
Pole Pairs |
7 |
||
Phase Resistance |
39 |
mΩ |
Phase-neutral |
Phase Inductance |
24 |
uH |
Phase-neutral |
Continuous Current |
50 70 |
A A |
Free Air Forced Air |
Peak Current |
90 |
A |
3-second |
Thermistor |
NTC 10k 3435 |
D5065 270KV
Specification |
Value |
Unit |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Speed Constant |
270 |
RPM/V [1] |
|
Torque Constant |
0.031 |
Nm/A [2] |
|
Speed / Torque Gradient |
515.67 |
RPM/Nm |
|
Pole Pairs |
7 |
||
Phase Resistance |
39 |
mΩ |
Phase-neutral |
Phase Inductance |
16 |
uH |
Phase-neutral |
Continuous Current |
45 65 |
A A |
Free Air Forced Air |
Peak Current |
85 |
A |
3-second |
Thermistor |
NTC 10k 3435 |
D5312s 330KV
Specification |
Value |
Unit |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Speed Constant |
330 |
RPM/V [1] |
|
Torque Constant |
0.025 |
Nm/A [2] |
|
Speed / Torque Gradient |
730.83 |
RPM/Nm |
|
Pole Pairs |
7 |
||
Phase Resistance |
37 |
mΩ |
Phase-neutral |
Phase Inductance |
23 |
uH |
Phase-neutral |
Continuous Current |
30 50 |
A A |
Free Air Forced Air |
Peak Current |
60 |
A |
3-second |
Thermistor |
NTC 10k 3435 |
NEMA 34 Servomotor w/ 16384 CPR Absolute Encoder
Specification |
Value |
Unit |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Speed Constant |
87 |
RPM/V [1] |
|
Torque Constant |
0.095 |
Nm/A [2] |
|
Speed / Torque Gradient |
81.00 |
RPM/Nm |
|
Pole Pairs |
4 |
||
Phase Resistance |
59 |
mΩ |
Phase-neutral |
Phase Inductance |
140 |
uH |
Phase-neutral |
Continuous Current |
20 |
A |
Free Air |
Peak Current |
40 |
A |
3-second |
Thermistor |
NTC 10k 3950 |
||
Integrated Encoder |
ODrive Botwheel
Specification |
Value |
Unit |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Speed Constant |
8.7 |
RPM/V [1] |
|
Torque Constant |
0.951 |
Nm/A [2] |
|
Speed / Torque Gradient |
10.98 |
RPM/Nm |
|
Pole Pairs |
15 |
||
Phase Resistance |
0.8 |
Ω |
Phase-neutral |
Phase Inductance |
1.7 |
mH |
Phase-neutral |
Continuous Current |
5 |
A |
Free Air |
Peak Current |
15 |
A |
3-second |
Thermistor |
NTC 20k 3950 |
||
Integrated Encoder |
Hall Sensors + 3200CPR Incremental Encoder |
[1] All voltage units are line-line amplitude
[2] All current units are phase amplitude
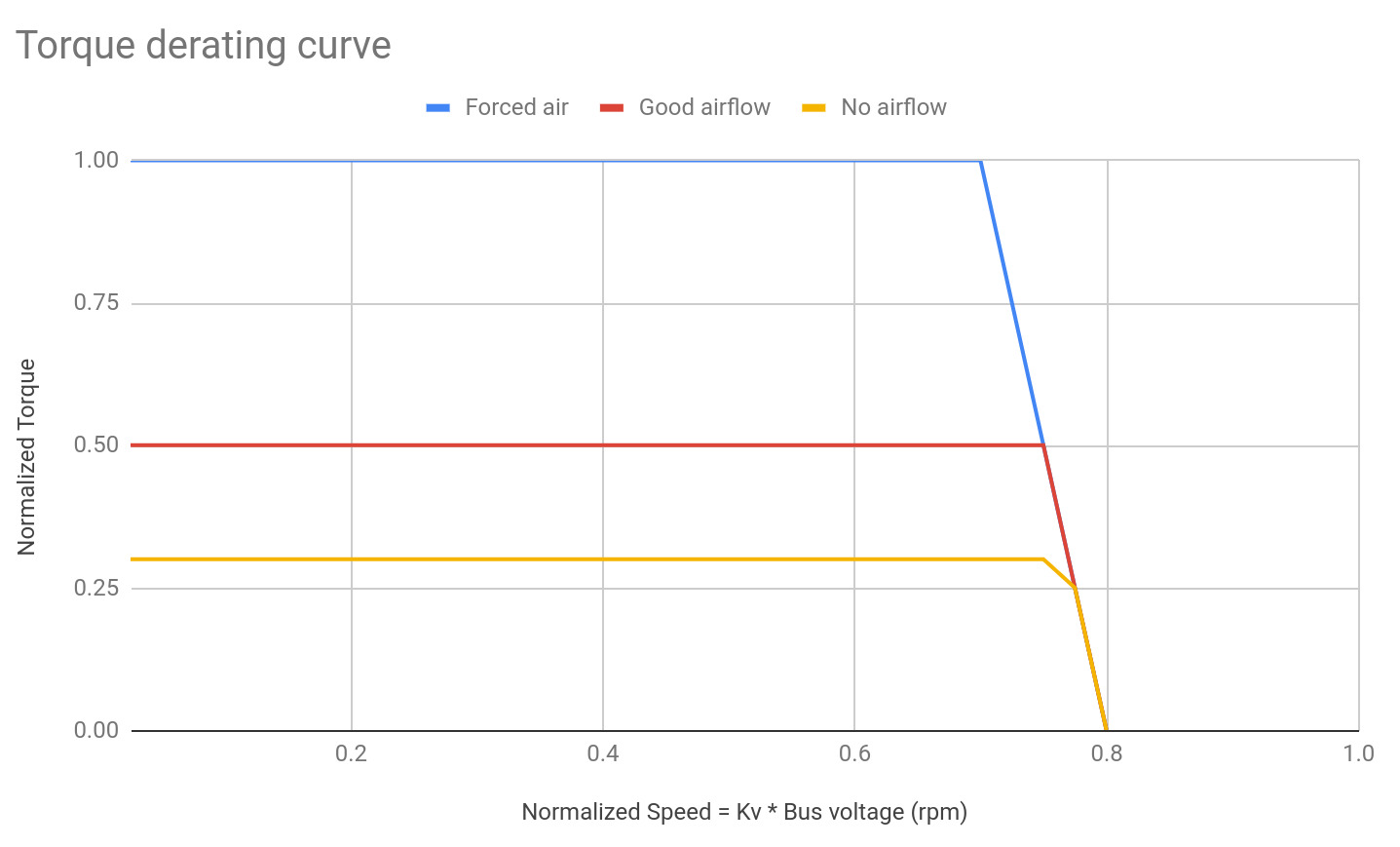
Torque-Speed Curves
Because brushless motors are current-limited devices, the torque-speed curve looks quite different than what many people are used to when dealing with brushed motors.
Specifically, the motor is able to operate at a constant torque for the vast majority of its speed range, with the specific torque determined by the motor’s torque constant and current rating. However, after a certain speed (“base speed”), the achievable torque linearly falls to zero as the motor reaches its no-load speed (“free speed”). An example of such a graph is below, however the exact response will differ based on the motor parameters.
Approximate torque-speed curves for various motors can be created with this calculator. The x-axis is the motor’s speed (in RPM), and the y-axis is the motor’s torque (in Nm). The green dotted line is the motor’s peak torque output, and the red solid line is the motor’s continuous torque output. Note this is only a rough model of motor behavior, intended as a guide for motor and ODrive selection — your real-world results may vary!
The default values in the calculator are for the ODrive D6374 150KV with an ODrive S1. To configure the plot for a different motor or ODrive:
Set \(K_{v}\) to the motor’s speed constant, in RPM/V.
Set \(R_{phase}\) to the motor’s phase-neutral resistance, in ohms (e.g. 24 mΩ = 0.024 Ω).
Set \(V_{bus}\) to your DC bus voltage, in volts.
Set \(M_{max}\) to your ODrive’s maximum modulation depth. * This is typically 0.78 for ODrive S1 and ODrive Micro, and 0.99 for ODrive Pro.
Set \(I_{peak}\) and \(I_{cont}\) to your motor’s peak and continuous current, in amps.
For instance, the below graph simulates an ODrive S1 + D6374 150KV with a 48V bus voltage.

We can see that the motor can output a continuous torque of about 2.756 Nm from zero speed to about 5,177 RPM (the “base speed”). From there, the achievable torque falls linearly approaching a free speed of 5,616 RPM. At its peak output (during short periods of time and intermittent operation), the motor can output about 4.96 Nm from zero speed to about 4,826 RPM, after which the achievable torque also falls linearly to the free speed of 5,616 RPM.